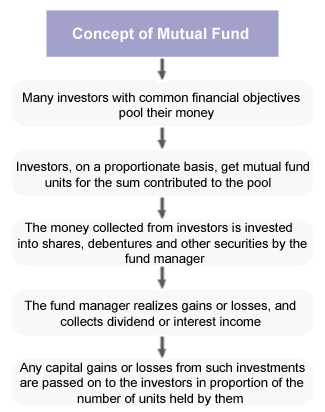
|
Advantages of Investing in Mutual Funds:
-
Portfolio
diversification
Mutual Funds invest in a number
of companies across a broad cross-section of
industries and sectors. This diversification reduces
the risk because seldom do all stocks decline at the
same time and in the same proportion. You achieve
this diversification through a Mutual Fund with far
less money than you can do on your own.
-
Tax benefits
Dividends given by equity
oriented mutual funds are tax-free in the hands of
the investor. In case of Debt funds, the funds pay
dividend distribution tax.
-
Flexibility
Mutual fund offers features
such as regular investment plans, regular withdrawal
plans and dividend reinvestment plans, you can
systematically invest or withdraw funds according to
your needs and convenience.
-
Liquidity
In open-end schemes, the
investor gets the money back promptly at net asset
value related prices from the Mutual Fund. In
closed-end schemes, the units can be sold on a stock
exchange at the prevailing market price or the
investor can avail of the facility of direct
repurchase at NAV related prices by the Mutual Fund.
-
Professional Management
Mutual Funds provide the
services of experienced and skilled professionals,
backed by a dedicated investment research team that
analyses the performance and prospects of companies
and selects suitable investments to achieve the
objectives of the scheme.
-
Low Costs
Mutual Funds are a relatively
less expensive way to invest compared to directly
investing in the capital markets because the
benefits of scale in brokerage, custodial and other
fees translate into lower costs for investors.
TYPES
OF MUTUAL FUNDS
General Classification of Mutual Funds
|
Open-end Funds | Closed-end Funds |
|
Open-end Funds
Funds that can sell and purchase units at any
point in time are classified as Open-end Funds.
The fund size (corpus) of an open-end fund is
variable (keeps changing) because of continuous
selling (to investors) and repurchases (from the
investors) by the fund. An open-end fund is not
required to keep selling new units to the
investors at all times but is required to always
repurchase, when an investor wants to sell his
units. The NAV of an open-end fund is calculated
every day.
Closed-end Funds
Funds that can sell a fixed number of units only
during the New Fund Offer (NFO) period are known
as Closed-end Funds. The corpus of a Closed-end
Fund remains unchanged at all times. After the
closure of the offer, buying and redemption of
units by the investors directly from the Funds is
not allowed. However, to protect the interests of
the investors, SEBI provides investors with two
avenues to liquidate their positions:
1.
Closed-end Funds are listed on the stock exchanges
where investors can buy/sell units from/to each
other. The trading is generally done at a discount
to the NAV of the scheme. The NAV of a closed-end
fund is computed on a weekly basis (updated every
Thursday).
2.
Closed-end Funds may also offer "buy-back of
units" to the unit holders. In this case, the
corpus of the Fund and its outstanding units do
get changed. |
|
Load Funds | No-load Funds |
|
Load Funds
Mutual Funds incur various expenses on marketing,
distribution, advertising, portfolio churning,
fund manager's salary etc. Many funds recover
these expenses from the investors in the form of
load. These funds are known as Load Funds. A load
fund may impose following types of loads on the
investors:
-
Entry Load -
Also known as Front-end load, it refers to the
load charged to an investor at the time of his
entry into a scheme. Entry load is deducted from
the investor's contribution amount to the fund.
-
Exit Load -
Also known as Back-end load, these charges are
imposed on an investor when he redeems his units
(exits from the scheme). Exit load is deducted
from the redemption proceeds to an outgoing
investor.
-
Deferred Load -
Deferred load is charged to the scheme over a
period of time.
-
Contingent Deferred Sales Charge (CDSC) -
In some schemes, the percentage of exit load
reduces as the investor stays longer with the
fund. This type of load is known as Contingent
Deferred Sales Charge.
No-load Funds
All those funds that do not charge any of the
above mentioned loads are known as No-load Funds.
|
|
Tax-exempt Funds | Non-Tax-exempt Funds |
|
Tax-exempt Funds
Funds that invest in securities free from tax are
known as Tax-exempt Funds. All open-end equity
oriented funds are exempt from distribution tax
(tax for distributing income to investors). Long
term capital gains and dividend income in the
hands of investors are tax-free.
Non-Tax-exempt Funds
Funds that invest in taxable securities are known
as Non-Tax-exempt Funds. In
India,
all funds, except open-end equity oriented funds
are liable to pay tax on distribution income.
Profits arising out of sale of units by an
investor within 12 months of purchase are
categorized as short-term capital gains, which are
taxable. Sale of units of an equity oriented fund
is subject to Securities Transaction Tax (STT).
STT is deducted from the redemption proceeds to an
investor. |
Broad Mutual Fund Types
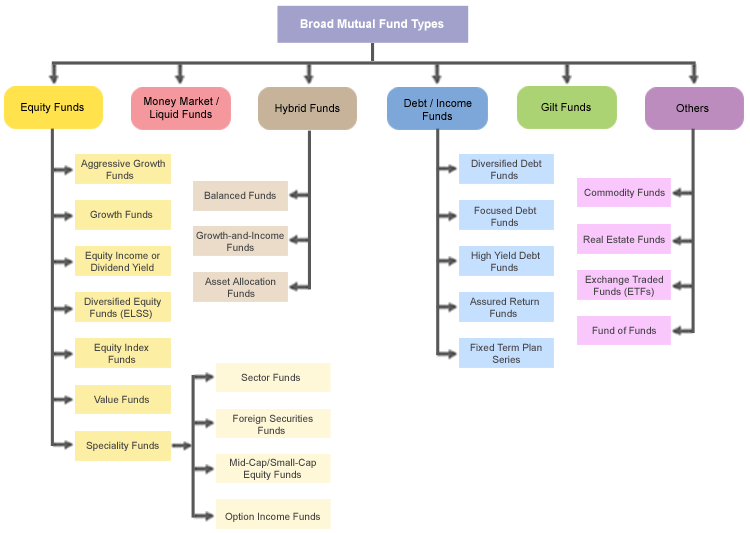
Mutual Fund Schemes
With an increase in interest and awareness about mutual funds amongst investors, there has also been a steady increase in the number of mutual fund schemes offered in India by as many as 35 Asset Management Companies (as on 1st January 2007).
Different schemes are introduced to suit different needs of investors. Mutual funds schemes may have different investment objectives which can be to earn recurring income for investors or growth of their invested capital or both. So investors should choose a scheme whose investment objective matches their personal objectives. To achieve the scheme's investment objectives, the fund manager, as per his own understanding, invests in a portfolio of asset classes which he thinks may provide the best returns to investors in the future. Different assets are exposed to a different level of risk. For example, investing in equities is riskier than investing in debt and investing in debt is slightly riskier than investing in money-market instruments. However, riskier investment options have a higher potential to provide higher returns.
Mutual Fund Schemes Comparison
Below is a comparison between different mutual fund schemes on the basis of their investment objectives, portfolio of investments and the level of risk associated. |
|
Equity Funds |
|
Types |
Investment Objectives |
Portfolio of Investments |
Risk Associated |
|
Aggressive Growth Funds |
Capital Appreciation |
Invest in less researched shares of
speculative nature |
Highly Volatile |
|
Growth Funds |
Capital Appreciation |
Invest in companies that are expected to
outperform the market in the future |
Volatile but less than Aggressive growth
funds |
|
Specialty Funds |
Capital Appreciation |
They follow a stated criteria for
investments and their portfolio comprises of only
those companies that meet their criteria. |
Concentrated and hence are riskier than
diversified funds |
|
Diversified Equity Funds |
Capital Appreciation |
A small portion of investment in liquid
money market, diversified equity funds invest
mainly in equities without concentration on a
particular sector. |
Well diversified and reduce sector-specific
or company-specific risk |
|
Equity Index Funds |
Capital Appreciation |
Portfolio of these funds comprises of the
same companies that form the index and is
constituted in the same proportion as the index. |
Risk associated is the same as that of the
benchmark index. Broader indices (like S&P CNX
Nifty or BSE Sensex) are less risky than narrow
indices (like BSEBANKEX or CNX Bank Index) |
|
Value Funds |
Capital Appreciation |
Value funds invest in those companies that
have sound fundamentals and whose share prices are
currently under-valued. |
These funds are exposed to a lower risk
level as compared to growth funds or specialty
funds |
|
Equity Income or Dividend Yield Funds |
To generate high recurring income and
steady capital appreciation |
Investments are made in those companies
which issue high dividends (such as Power or
Utility companies). |
These funds are generally exposed to the
lowest risk level as compared to other equity
funds |
|
Income / Debt Funds
and
Money Market Funds |
|
Types |
Investment Objectives |
Portfolio of Investments |
Risk Associated |
|
Diversified Debt Funds |
To generate fixed current income |
These funds invest in all securities issued
by entities belonging to all sectors of the market |
Low volatility, default risk remains |
|
High Yield Debt funds |
To earn higher interest returns |
Invest in securities issued by those
issuers who are considered to be of "below
investment grade" |
More volatile and bear higher default risk
than diversified debt funds |
|
Assured Return Funds |
To offer assurance of annual returns to
investors through out the stated lock-in period |
Predominantly debt securities |
A low-risk investment opportunity |
|
Fixed Term Plan Series |
To generate some expected returns in a
short period |
Usually invest in debt / income schemes |
Low risk fund |
|
Money-Market Funds |
Recurring income and capital safety |
Invest in short-term (maturing within one
year) interest bearing debt instruments |
Safest mutual fund investment option,
interst rate risk remains |
|
Hybrid Funds |
|
Types |
Investment Objectives |
Portfolio of Investments |
Risk Associated |
|
Balanced Funds |
To generate regular income, moderate
capital appreciation and at the same time
minimizing the risk of capital erosion |
Debt securities, convertible securities,
and equity and preference shares held in a
relatively equal proportion |
Limited risk to principal and moderate
long-term growth |
|
Growth-and-Income Funds |
Capital growth and some current income |
These funds invest in companies having
potential for capital appreciation and those known
for issuing high dividends |
Safer as compared to growth funds and
riskier than income funds |
|
Asset Allocation Funds |
Capital Growth and income generation |
These funds invest in financial assets or
non-financial (physical) assets |
Success of these funds depends upon the
skills of a fund manager in anticipating market
trends |
4. Commodity Funds
Those funds that focus on investing in different
commodities (like metals, food grains, crude oil etc.)
or commodity companies or commodity futures contracts
are termed as Commodity Funds. A commodity fund that
invests in a single commodity or a group of commodities
is a specialized commodity fund and a commodity fund
that invests in all available commodities is a
diversified commodity fund and bears less risk than a
specialized commodity fund. "Precious Metals Fund" and
Gold Funds (that invest in gold, gold futures or shares
of gold mines) are common examples of commodity funds.
5. Real Estate Funds
Funds that invest directly in real estate or lend to
real estate developers or invest in shares/securitized
assets of housing finance companies, are known as
Specialized Real Estate Funds. The objective of these
funds may be to generate regular income for investors or
capital appreciation.
6. Exchange Traded Funds (ETF)
Exchange Traded Funds provide investors with combined
benefits of a closed-end and an open-end mutual fund.
Exchange Traded Funds follow stock market indices and
are traded on stock exchanges like a single stock at
index linked prices. The biggest advantage offered by
these funds is that they offer diversification,
flexibility of holding a single share (tradable at index
linked prices) at the same time. Recently introduced in
India, these funds are quite popular abroad.
7. Fund of Funds
Mutual funds that do not invest in financial or physical
assets, but do invest in other mutual fund schemes
offered by different AMCs, are known as Fund of Funds.
Fund of Funds maintain a portfolio comprising of units
of other mutual fund schemes, just like conventional
mutual funds maintain a portfolio comprising of
equity/debt/money market instruments or non financial
assets. Fund of Funds provide investors with an added
advantage of diversifying into different mutual fund
schemes with even a small amount of investment, which
further helps in diversification of risks. However, the
expenses of Fund of Funds are quite high on account of
compounding expenses of investments into different
mutual fund schemes.
| |
Make market
timings irrelevant |
You have
always tried to find the best time to invest in the market… but
without success.
When the market is falling you feel that it may decline further
and you wait a while. Suddenly the market recovers even before
you notice and the opportunity is lost.
When markets are rising, you wait for the correction to happen.
But the correction doesn’t come about. Again, an opportunity is
missed! |
| |
Now stop missing
the opportunities...How? |
| |
Buy less when
markets are rising and more when markets fall. You can do this
without any effort using Systematic investment plan (SIP). which
invests a fixed amount every month in the markets. Let’s take an
example: say, every month you commit to invest Rs. 10,000 in a
mutual fund scheme. |
| |
|
| |
| Date |
Sensex Levels |
NAV(Rs.) |
Amount (Rs.) |
Units |
| 2- Dec |
20,044 |
104 |
10,000 |
96 |
| 2- Jan |
20,926 |
113 |
10,000 |
89 |
| 2- Feb |
19,080 |
92 |
10,000 |
109 |
| 2- Mar |
17,053 |
84 |
10,000 |
120 |
| 2- Apr |
16,105 |
78 |
10,000 |
129 |
| 2- May |
17,996 |
86 |
10,000 |
116 |
| 2- Jun |
16,425 |
80 |
10,000 |
126 |
| 2- Jul |
13,972 |
71 |
10,000 |
140 |
| 2- Aug |
14,906 |
74 |
10,000 |
134 |
| 2- Sep |
15,388 |
75 |
10,000 |
133 |
| Total |
100,000 |
1,192 |
Average Cost
per unit |
84 |
|
| |
|
| |
As seen in
the table in July when the market was at 13,972 levels, units
bought from Rs.10,000 were 140 units which is far more than 89
units bought when market was at 20,926 levels.Thus through SIP
more units were bought at lower levels and less at market peaks. |
|
| |
So for your
1,192 units bought through the route of SIP your average per
unit cost turns out to be Rs.84. If you had bought all 1,192
units in the month of January, the cost per unit would have
increased to Rs.113. |
| |
|
| |
Points to
consider before deciding on a SIP |
|
Ascertain
your investment horizon
Decide on the periodicity of investment
Determine the amount you can comfortably invest in a SIP
periodically
Pick a scheme according to your risk profile
Invest for the long term |
|
Start an SIP as low as Rs.500/- |
|
|
|
|